The status quo of security alliances of enterprises The strategic alliance of enterprises refers to the long-term cooperation arrangements between two or more enterprises in order to achieve some common strategic goals. Its uniqueness lies in making the enterprises in the alliance complement each other and share resources. While enhancing the overall core competitiveness of the alliance companies, it does not weaken the original core competitiveness of each enterprise and achieve the goal of “win-win†or “win-winâ€. At present, China's security industry mainly has three forms of alliance: sales alliances, industry alliances, and standards alliances.
Sales Alliance Sales Alliance refers to a cooperative alliance between security manufacturers, distributors, agents, and project providers. In the early development of the security industry, due to business needs, companies often spontaneously cooperate with each other, for example, when several companies pick up each other, notify each other of prices, and collaborate with orders to reduce transaction costs. This kind of cooperation is mainly linked to “human emotions†and “relationships,†and it lacks an effective restraint mechanism and has strong uncertainty. On the one hand, the loosely federated approach tends to generate interest disputes. Once the impasse is reached, the alliance is easily disbanded. On the other hand, with the reduction of living space, each sales segment will compete for profit, creating pressure on each other.
In recent years, with the establishment of alliances such as Shangzhi Alliance and South Self-Security Project, the scale of sales alliances in the security industry has gradually expanded, and the alliance is increasingly standardized, showing a mature trend.
Industry alliances Industry alliances are mostly groups led by third parties and companies participate in, such as the Security Association, the Enterprise Building Industry Intercom Industry Alliance, and the Alarm Service Industry Alliance. Such a coalition is a macroscopic and guiding coalition that plays an important role in broadening business information exchange channels in the industry and guiding the direction of industry development. However, it does not involve enterprise operations, it is difficult to form a strategic synergy effect, and it cannot give rise to the company’s core competitiveness. Come to help directly.
In 2008, the establishment of the global security industry alliance, jointly sponsored by the China Security Industry Association, the U.S. Security Industry Association, the Russian Security Industry Association, the Brazilian Security Industry Association, and the Shenzhen Security Association, marked the expansion of the regional security industry alliance to internationalization. development of.
Standard alliance security industry enterprises in order to ensure compatibility between products, will form a certain standard alliances, such as ONVIF (Open Network Video Interface Forum), digital professional walkie-talkie standard alliance. This alliance approach has a good effect on unifying industry standards, improving overall technical strength, and avoiding waste of resources. This type of alliance has a short development time in China. Some important standards are mainly in the hands of foreign companies.
In general, the level of strategic alliances in China's security industry is relatively low, and a corporate alliance that can really produce strategic synergies and promote the development of the core competitiveness of domestic enterprises has not yet emerged.
The urgency to enhance the level of strategic alliances With the rapid advancement of national security construction, the security industry has entered an unprecedented stage of rapid development. Changes in the market, advances in technology, and fierce competition have all made the upgrading of strategic alliances more and more urgent.
The rapid expansion of the market has spawned high-level strategic alliances. In recent years, on the one hand, with the rollout of safe city construction, environmental monitoring, traffic monitoring and other projects and the promotion of large-scale security projects such as the Olympics and the World Expo, the security market is rapidly expanding. On the other hand, the improvement of user requirements makes integration of security services more important. The current security project can no longer be completed by a single company, and cooperation has become inevitable. It can be predicted that the future sales alliance will show a more standard and close trend. Only in this way can the cooperation of enterprises play a role of 1+1>2, which reflects the overall core competitiveness of the alliance, and the survival of those enterprises that are separated from the alliance and go it alone will become very difficult.
The rapid development of technology calls for high-level strategic alliances. The continuous improvement of product technical requirements poses a challenge to the R&D strength of enterprises. Enterprises need to take advantage of the technological development trends represented by digitalization, networking, integration, and intelligence in the future. Not only does it have to strengthen its technical research and development capabilities, but it must also strengthen its guidance and control over the latest technologies in the industry. As for SMEs that are currently not technologically superior, they need to expand their own information channels and speed up their technological content through alliances in order not to be eliminated in the fast-growing technology market. Under the technological alliance, corporate cooperation R&D can not only reduce the R&D costs of individual companies, but also accelerate the speed of R&D through brainstorming and wider information channels.
The fierce competition between internal and external risks requires a high-level strategic alliance. Foreign-funded enterprises in the Chinese security industry currently have absolute advantages. Even the core technologies of some enterprises that hold national brands still come from foreign-funded enterprises. At present, foreign-funded enterprises are strengthening their control over the industry with their stronger financial strength and technological advantages. For Chinese companies, in the face of the inflow of foreign-funded enterprises, they have not experienced the internal frictions of price wars and cost wars. Only by uniting can they exert their strengths to play an advantage in competition with foreign capital.
Relevant Thinking and Suggestions for Corporate Strategic Alliances For security companies, first of all, they must open their minds to strengthen their learning and innovation capabilities and actively participate in industry alliances. Second, companies should be good at confronting conflicts in the coalition, distinguishing between destructive conflicts and constructive conflicts, and recognizing that occasional conflicts may be conducive to the development of mutually beneficial cooperation and new ideas. Third, companies should rationally analyze their own work content, and in the process of implementing the alliance, study how to effectively use the advantages and resources of strategic partners, and further enhance alliance functions based on the principles of integrity and cooperation. Finally, companies also need to consider how to make their core technologies competitive when the alliance works.
At present, the polarization of China's security industry companies is relatively large. In this situation, companies of different sizes should adopt different strategies in participating in the process of corporate alliances.
For some enterprises with certain technological advantages in the industry, the dominant industry alliance is an opportunity to increase the control of the industry on the industry. For enterprises that are currently at the advanced level in the industry, they should focus on technology and actively lead industry alliances. Specifically, this group of companies can play a role in the government alliance, standardize the alliance, and make it legal. At the same time, it uses its influence and appeal to attract companies in the industry. In addition, in the selection of partners, companies should Pay attention to the complementary advantages, you can also try to improve product technology through cooperation with universities and research institutes. This part of the enterprise should also open up its horizons, look globally, and learn to compete at a higher level.
For SMEs, participating in industry alliances is an important way to increase their own strength. For SMEs with relatively backward technology, relatively low-end products, and low output value, joining a corporate alliance is an important way to obtain industry-related information. This part of the enterprise must first change the concept of competition, turn adversarial competition into cooperative competition, and abandon the traditional development model of “big and full†and “small but comprehensive†and continuously improve the level of socialization. Only in this way can faster development be achieved.
Concluding remarks Once there was a blind pursuit of “low prices,†and the evasion of technology development allowed SMEs to taste the bitterness in this environment of militarism. China's security industry has two major "hard injuries." In the front-end market, the government’s administrative power dominates, and companies’ control of the project is weak. In the back-end market, the core technology of SMEs is in the hands of foreign companies and has poor control over the overall industry chain. The current security industry has reached a critical period of competition from market competition to technology. Enterprises in the security industry only have a clear understanding of the situation, strengthen cooperation, and upgrade the alliance level in order to achieve better advantages in future competition.
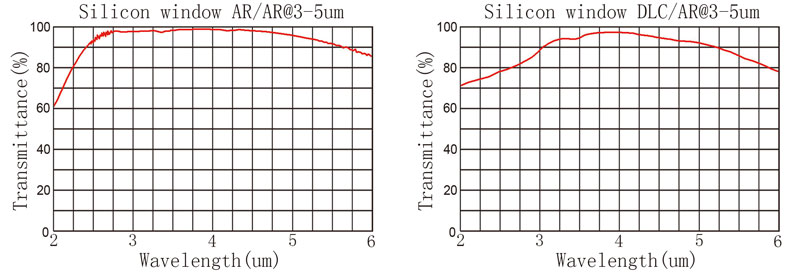
The refractive index of the monocrystalline silicon material is about 3.42, and the reflectivity of the silicon lens after polishing is about 30% in the air environment. Our common silicon lens and silicon window can be coated on the surface (Antireflection Coating), which can reduce the reflectivity to less than 1.5% between 3 to 5 um.
Some silicon elements, especially the silicon protected windows, are exposed to dust, acid, salt and so on in the harsh environment. The conventional multilayer antireflection coating will be damaged and affect the normal work of the equipment. At this time, we need to make DLC coating on the surface of the silicon lens.
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) Coated Silicon Windows are engineered for 3 to 5µm, making them ideal for infrared defense applications such as thermal imaging.
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) Coated Silicon Windows provide anti-reflection coating on one surface and a specially designed DLC coating on the other surface, making these windows highly durable and ideal for harsh environments.
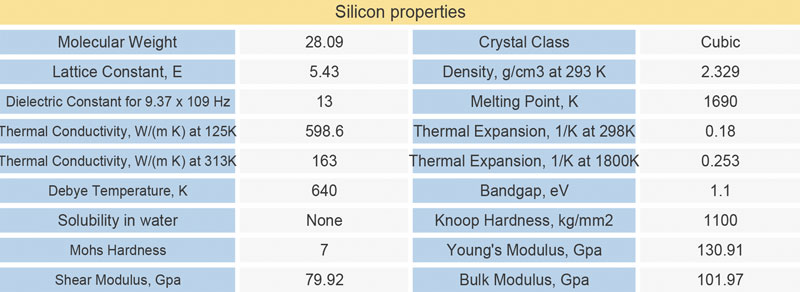
| Silicon lens specifications: | ||
| Standard precision | High-precision | |
| Dimension Tolerance | φ5-250mm+0/-0.2 | φ3-350mm+0/-0.2 |
| Thickness Tolerance | 1-50mm+/-0.1 | 1-50mm |
| Centration | 3 arc minute | 1 arc minute |
| Surface Quality | 60/40 | 20/10 |
| Power(fringe@633nm) | N<λ/2@633nm(in 25mm) | N<λ/10@633nm(in 25mm) |
| Clear Aperture | >90% | >95% |
| Chamfer | Protected <0.5mmx45deg | Protected <0.5mmx45deg |
Silicon Lens,Silicon Optical Lens,Infrared Si Lens,Silicon Plano-Convex Lens
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.opticsrealpoo.com