In the fastener industry for so many years, do you know the meaning of the label on the fastener?

The bolts for steel structure connection are classified into more than 10 grades of 3.6, 4.6, 4.8, 5.6, 6.8, 8.8, 9.8, 10.9, 12.9, etc., of which the bolts of grade 8.8 and above are made of low carbon alloy steel or medium carbon steel. Heat treatment (quenching, tempering), commonly known as high-strength bolts, the rest are commonly referred to as ordinary bolts. The bolt performance grade label is composed of two parts, which represent the nominal tensile strength value and the yield ratio of the bolt material. E.g:
   Bolts with a performance class of 4.6, which means:
1. The nominal tensile strength of bolt material is up to 400MPa;
2. The yield ratio of the bolt material is 0.6;
3. The nominal yield strength of the bolt material is 400×0.6=240MPa.
  Performance grade 10.9 high strength bolts, after heat treatment, can achieve:
1. The nominal tensile strength of bolt material is up to 1000MPa;
2. The yield ratio of the bolt material is 0.9;
3. The nominal yield strength of the bolt material is 1000×0.9=900MPa.
The meaning of the bolt performance grade is the international standard. The bolts of the same performance grade have the same performance regardless of the difference between the material and the place of origin. Only the performance grade can be selected in the design.
Strength grades The so-called grades 8.8 and 10.9 refer to bolts with shear stress ratings of 8.8 GPa and 10.9 GPa.
8.8 The nominal tensile strength is 800N/MM2, and the nominal yield strength is 640N/MM2.
The general bolt is expressed by "XY", X*100=the tensile strength of this bolt, X*100*(Y/10)=the yield strength of this bolt (because it is specified according to the label: yield strength/tensile strength) =Y/10).
If the grade is 4.8, the tensile strength of the bolt is: 400MPa; the yield strength is: 400*8/10=320MPa.
Another: stainless steel bolts are usually marked as A4-70, A2-70, the meaning is explained otherwise.
Measurement: There are two main types of length measurement units in the world today. One is metric, and the measurement units are meters (m), centimeters (cm), millimeters (mm), etc., which are used in Southeast Asia such as Europe, China, and Japan. The other is the British system, the measurement unit is mainly inches (inch), which is equivalent to the old city market in China, and is used more in the United States, Britain and other European and American countries.
1. Metric measurement: (10 decimal) 1m = 100 cm = 1000 mm
2, inch measurement: (8) 1 inch = 8 inches 1 inch = 25.4 mm 3 / 8 ¢¢ × 25.4 = 9.52
3, 1/4 ¢¢ or less products use the number to indicate its calling diameter, such as: 4#, 5#, 6#, 7#, 8#,10#,12#
   Spiral
1. A thread is a shape having a uniform spiral protrusion on a section of the outer or inner surface of the solid.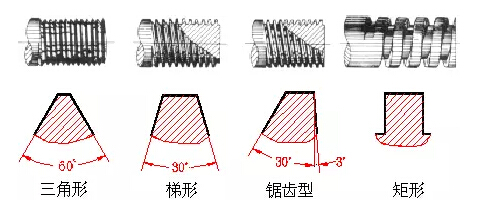
According to its structural characteristics and uses, it can be divided into three categories:
(A), ordinary thread: the tooth shape is a triangle, used to connect or fasten parts. Ordinary threads are divided into coarse teeth and fine thread according to the pitch, and the connection strength of the fine thread is high.
(2) Transmission thread: The tooth shape has a trapezoidal shape, a rectangular shape, a saw shape and a triangular shape.
(3) Sealing thread: used for sealing connection, mainly for threading, taper thread and taper pipe thread.
Second, the thread matching level:
The thread fit is the loose or tight size between the threaded threads, and the level of fit is the specified combination of deviations and tolerances on the inner and outer threads.
(1) For uniform inch thread, the external thread has three thread grades: 1A, 2A and 3A, and the internal thread has three grades: 1B, 2B and 3B, all of which are clearance fit. The higher the level number, the tighter the fit. In the inch thread, the deviation only specifies the 1A and 2A levels, the 3A level deviation is zero, and the 1A and 2A level deviations are equal. The larger the number of grades, the smaller the tolerance.
1, 1A and 1B grade, very loose tolerance class, which is suitable for tolerance fit of internal and external threads.
2, 2A and 2B, is the most common thread tolerance class specified by the British series of mechanical fasteners.
3, 3A and 3B, screwing to form the tightest fit, suitable for tight tolerance fasteners, for critical design of safety.
4. For external threads, 1A and 2A have a tolerance, and 3A does not. The 1A tolerance is 50% larger than the 2A tolerance and 75% larger than the 3A. For the internal thread, the 2B tolerance is 30% greater than the 2A tolerance. Level 1B is 50% larger than 2B and 75% larger than 3B.
(2) Metric threads, external thread has three thread grades: 4h, 6h and 6g, internal thread has three thread grades: 5H, 6 H, 7H. (The Japanese standard thread accuracy grade is divided into three grades I, II, and III, and the normal grade is grade II.) In the metric thread, the basic deviation of H and h is zero. The basic deviation of G is a positive value, and the basic deviation of e, f, and g is a negative value. as the picture shows:
1. H is the common tolerance zone position for internal threads. It is generally not used as a surface coating or an extremely thin phosphating layer. The basic deviation of the G position is used for special occasions, such as thicker coatings, which are rarely used.
2, g is commonly used to plate 6-9um thin coating, such as the product drawing requirements of 6h bolts, the pre-plated thread uses a 6g tolerance band.
3, the thread fit is best combined into H / g, H / h or G / h, for bolts, nuts and other refined fastener threads, the standard is recommended to use 6H / 6g
Third, the main geometric parameters of self-tapping and self-drilling threads:
(1) Large diameter/tooth outer diameter (d1), which is the diameter of the imaginary cylinder where the thread crests coincide. The large diameter of the thread basically represents the nominal diameter of the thread size.
(B), small diameter / bottom diameter (d2): the diameter of the imaginary cylinder that coincides with the thread bottom.
(3), tooth distance (p): the axial distance of two points corresponding to the adjacent teeth on the meridian line. In the inch system, the tooth pitch is indicated by the number of teeth per inch (25.4 mm).
  The table below lists the common pitch (metric) teeth (inch)
1. Metric self-tapping:
Specifications: ST 1.5, S T1.9, S T2.2, S T2.6, S T2.9, S T3.3, S T3.5, S T3.9, S T4.2, S T4.8, S T5.5, S T6.3, S T8.0, S T9.5
Teeth: 0.5, 0.6, 0.8, 0.9, 1.1, 1.3, 1.3, 1.3, 1.4, 1.6, 1.8, 1.8, 2.1, 2.1
2, the British system self-tapping:
Specifications: 4#, 5#, 6#, 7#, 8#, 10#, 12#, 14#
Number of teeth: AB teeth 24, 20, 20, 19, 18, 16, 14, 14
A tooth 24, 20, 18, 16, 15, 12, 11, 10
Ridge Cap Roll Forming Machine is a common and popular machine in the field.
Ridge Caps, Ridge Rolls or Ridge Flashings are metal objects that cap the ridge of a roof.
For Metal Roof It has advantage of pretty appearance, durable using and so on. It is produced continuously as Roll Forming Machine instead using bending machine to make angel tile saving human resources, lower labor cost.The ridge caps are widely used in residential house,workshop,commercial building.
Ridge Cap Roll Forming Machine
Ridge Cap Roll Forming Machine,Ridge Cap Metal Roof Forming Machine,Steel Ridge Cap Roll Forming Machine, Automatic Ridge Cap Cold Roll Forming Machine
HEBEI HANMAC MACHINE CO., LTD. , https://www.chinahanmac.com