Definition of fatigue fracture:
The brittle fracture of a material under the action of alternating stress below the breaking strength is called fatigue, and the typical characteristics of fatigue strips (or fatigue striations) are often seen.
For the fatigue source area, the simplest is the convergence source area:
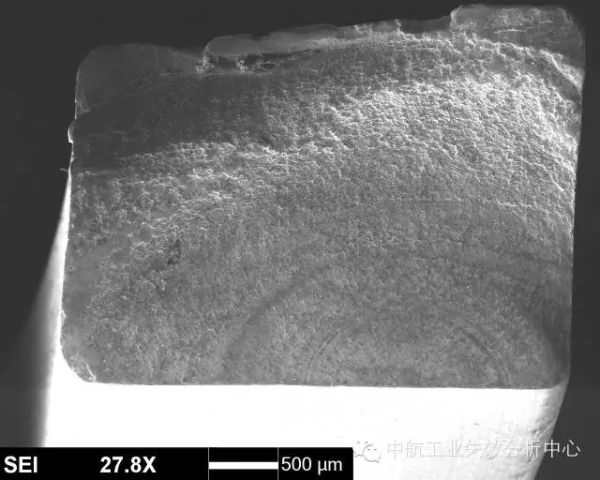
The source area is radioactive, and its convergence position is the source area.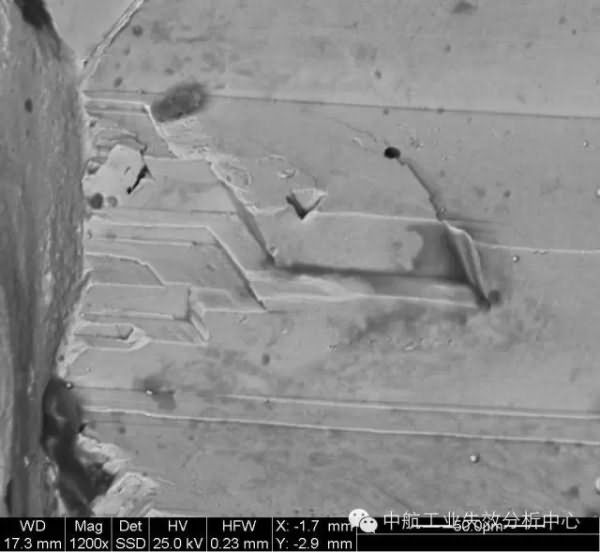
The source area is in the form of an arc, and its center position is the source area.The section near this source area is generally flat, and the undulation and roughness of the section will increase. The fatigue origin of the convergence class accounts for a large proportion of the fatigue failure. In the other case, the fatigue source region is the cleavage plane or the quasi/class cleavage plane interlacing, which is common in copper alloys and high-temperature alloys, and is also the case in some titanium alloys.
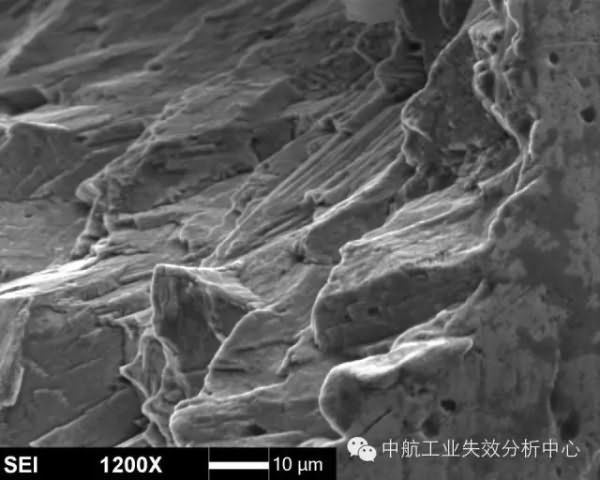
Cleavage characteristics of high temperature alloy source region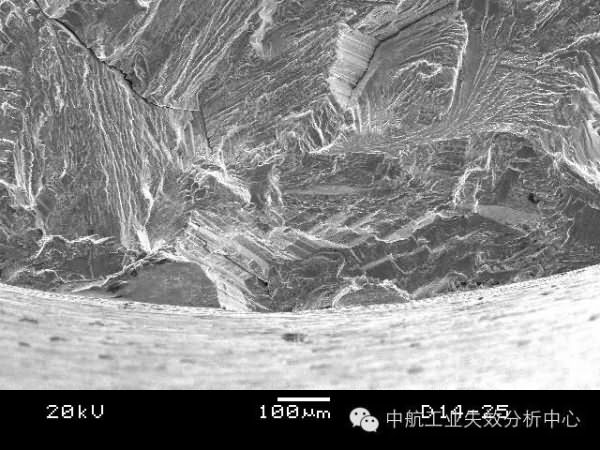
Cleavage-like characteristics of copper alloy source regions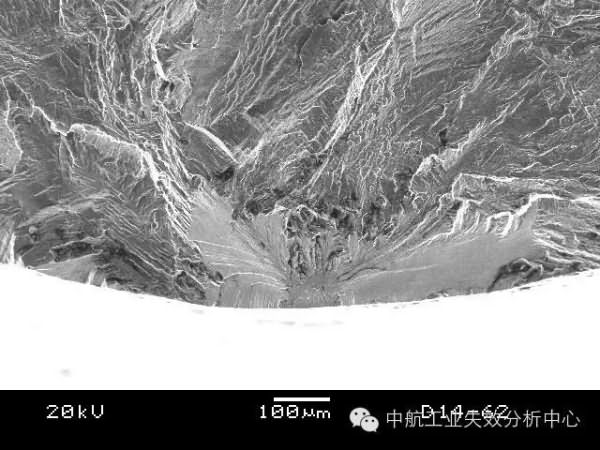
Cleavage characteristics of titanium alloy source regionThis kind of cross section near the source area is rough due to the staggered distribution of multiple cleavage planes, and then the fatigue expansion before and after the expansion is flat, and the rapid expansion after the instability again becomes undulating and rough. In addition, some fatigue does not necessarily originate from the surface of the sample, and may be inside the sample, which may be caused by internal defects or sub-surfaces in a special stress state.
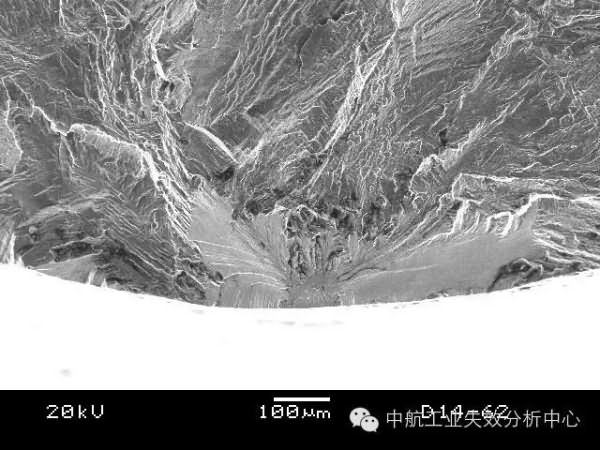
Some origins are not only originated in one location, but may generate fatigue sources in multiple locations. At this time, we can see similar step characteristics between multiple fatigue sources, which are caused by multiple cracks and expansion. In the process, it is impossible to expand on one plane. When the cracks meet each other, the different expansion planes must be connected by shear tearing to form a step.
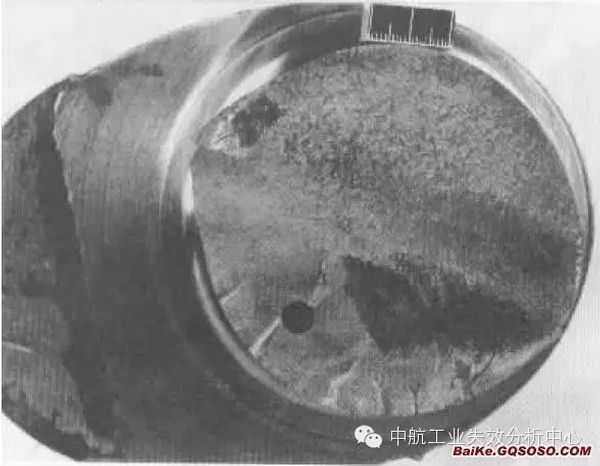

Multiple intersection steps at the edge of the sampleThe above said so much, is everyone fainting? How do you seem to have any patterns, how should we judge?
First of all, of course, it is judged by the convergence of the ridge line. After all, most of the fatigue has this feature.
Secondly, look at whether it is a special alloy of copper alloy and superalloy. For them, finding the cleavage surface is almost the same.
Again, focusing on the steps, the steps necessarily mean that there are multiple cracks that meet together, that is, there is a high probability that there is a source zone on both sides of a step.
Then, we have a few ways to help judge:First, the direction of the strip. Strip characteristics can be observed in almost all fatigue fractures. At this point, the center of the strip arc points to the source region. However, it should be noted that the strip is only a very microscopic feature, and it may cause a change in the direction in which the strip expands due to a change in stress at a local location. Therefore, this method can only be used as an auxiliary discriminating means.
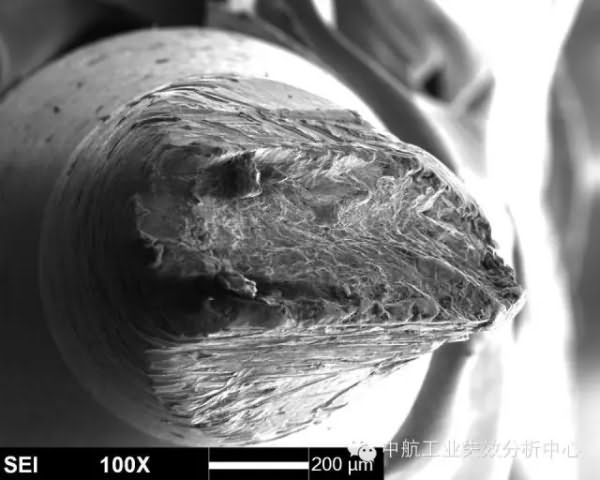

Second, the instantaneous break zone is discriminated. The source area is really difficult to find, you can go to the instantaneous break zone first, because the instantaneous fault zone is often dominated by the ductile fracture mode, and the dimple characteristics different from the fatigue zone are generally visible. In addition, the short-cut zone is mainly broken under the action of shearing force, and generally has a certain inclination angle with the main section, which is better to distinguish. After finding the instantaneous break zone, the opposite position is generally the source zone.

The left side of the fracture is the instantaneous break zone, from which the right side is the source zone.Seeing this, do you think you understand something? So let's examine ourselves below: Where is the source area of ​​the fracture below? How many source areas are there?
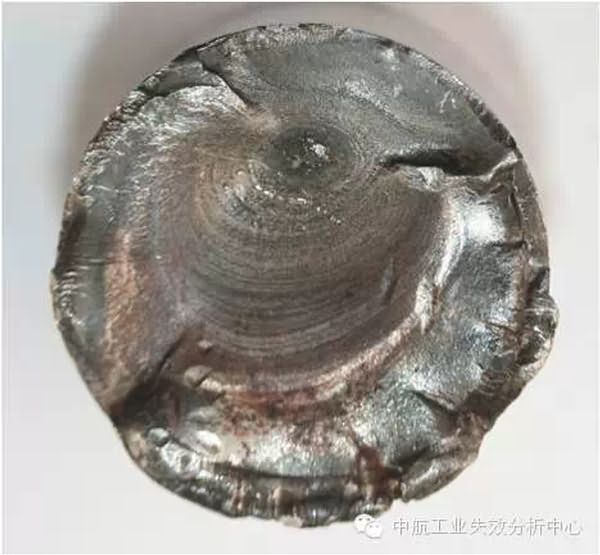

Source: AVIC Failure Analysis Center, author: Liu Chau.
Have a professional manufacturing base of mining equipment, many sets of excavators with the largest capacity up to 75m³. The excavators can be used in surface stripping, digging and truck loading in various of large open-pit mines, iron ore mines and non-ferrous metal mines.
dedicated to steel Hot/Cold Rolling Mill Equipment developed high-tech enterprises, the company has a number of independent research and development of the franchise, ultra-high-quality cost-effective in the industry chasing far ahead
Mining Shovle,Mining Workshop,Best Mining Workshop,Mining Workshop For Sale
Taiyaun JDS Machinery And Equipment Co., Ltd. , https://www.jdsmachine.com