Synthesis and Application of Polyamine-Based Aldehyde-Free Fixing Agents ZHANG Qingping, FAN Zenglu, ZHAI Feifei, CAI Jianfang, TANG Wenfeng (School of Textiles and Materials, Xi'an Polytechnic University, Xi'an 710048, China)
Abstract: A formaldehyde-free polyamine fixing agent was prepared by using dimethylamine, epichlorohydrin and tetraethylenepentamine as main raw materials. Through experiments, the optimal synthesis process and optimal fixing process of synthetic polyamine fixing agent were determined. The optimum synthesis process is as follows: after reacting dimethylamine and epichlorohydrin in a molar ratio of 1:1.5 for about 2 hours, adding 4% of tetraethylenepentamine in a total amount of monomers, reacting at 70 ° C 5h. The best fixing process is: dyeing cotton fabric leaves two dip two rolling (finishing agent 40g / L, rolling rate 80%) → drying (100 ° C). After finishing the fabric. The fastness of the direct dye can be improved by 1 to 2, and the effect on the shade is small.
Key words: fixing agent; synthesis; fixation; direct dye; cotton fabric CLC number: TS 193.225 Document code: A
Article ID:1674-649X(2010)06-0734-05
Direct dyes account for a large proportion of cotton dyeing due to complete chromatograms. However, due to the presence of water-soluble groups such as sulfonic acid groups and carboxyl groups in the molecular structure, the wet processing fastness is poor, and the fixing agent is indispensable for dyeing. Post-dyeing treatment [1-2]. Usually used fixing agent Y, coloring agent G, etc., can improve its color fastness, but these fixing agents contain free formaldehyde, which is harmful to the human body in the dyeing solution [3]. With the increasing demand for green textiles and environmental protection in the domestic and foreign markets, and the promulgation and implementation of ISO14000 [4-5], the development of environmentally-friendly fixing agents with high solid fastness has been a textile auxiliaries in recent years. The main direction of attack [6], but the current fixing agent that can improve the wet processing fastness to level 3 or above is still very limited [7]. The polyamine type fixing agent developed in this paper has the advantages of no formaldehyde emission, low cost and good fixing effect, and has good market development prospects.
1. Experiments 1.1 Raw materials and reagents Direct lake blue 5B dyed cotton cloth, dimethylamine (33%), epichlorohydrin, tetraethylene pentamine, formaldehyde-free fixing agent 2011.
1.2 Equipment Electric mixer, electric thermostatic water bath, rubbing fastness tester, wash fastness tester, SF-300 thinking computer colorimeter.
1.3 Method (1) Fixing agent synthesis A certain amount of dimethylamine is added to a three-necked bottle with a stirrer, placed in a cold water bath, the temperature in the flask is about 23 ° C, the stirrer is started, and the drop is used. The liquid funnel slowly drops the epichlorohydrin, and the drip acceleration is strictly controlled. The drip rate is 3~4s, and the drop is made. After the completion of the dropwise addition, the temperature rises to about 28 ° C, and the reaction is continued for 2 h. Then, tetraethylene pentamine is added dropwise. After the completion of the dropwise addition, the reaction is continued for 2 hours, and then the temperature is raised to 55 ° C to 75 ° C for 3 to 6 hours to obtain a synthesized product.
(2) Fixing process Direct dye dyed cotton fabric-padding fixing solidifying liquid (two dip two rolling)→drying.
1.4 Color fastness test 1.4.1 Determination of rubbing fastness The rubbing fastness is determined according to the method of CB/T3920-1997 (color fastness to rubbing of textile color fastness test).
1.4.2 Determination of the color fastness to soaping. The color fastness tester SW-12 was used, and it was determined by the method of GB/T3921-2008 (color fastness to soaping of textiles).
1.4.3 Grade of color fastness The grade of color fastness is evaluated according to GB/T251-1995 staining with gray sample card.
1.4.4 Test of color difference ΔL, △C, △E, △H of fabric were measured by SF-300 thinking computer colorimeter, and corresponding evaluation and analysis were carried out.
2. Results and discussion 2.1 Synthesis process of fixing agent According to the synthetic method of 1.3 fixing agent, the obtained series of products were respectively applied to direct lake blue 5B (dye concentration 10% O.W.f .) dyed cotton fabric for fixing treatment, testing the rubbing color fastness and wash fastness of cotton fabric after finishing. The fixing process of direct dyes is: dyed cotton fabric → two dip two ties (finishing agent 40g / L, rolling rate 80%) → drying (100 ° C).
2.1.1 Effect of molar ratio of dimethylamine and epichlorohydrin on fixing agent According to the synthesis method of 1.3 fixing agent, the synthesis experiment of dimethylamine and epichlorohydrin was carried out for 2 hours. The total mass of the monomer is 2% of tetraethylene pentamine. After 2 hours, the temperature is raised to 70 ° C. The molar ratio of dimethylamine to epichlorohydrin was changed, and the obtained series of products were respectively fixed to the cotton fabric dyed directly by Lake Blue 5B, and the color fastness was tested. The results are shown in Table 1. 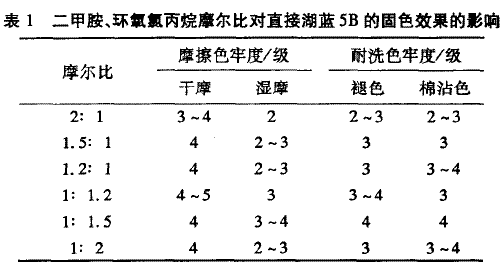
It can be seen from Table 1 that when the molar ratio of epichlorohydrin and dimethylamine is gradually increased, the color fastness is gradually increased; when the molar ratio of dimethylamine to epichlorohydrin is 1:1.5 The fixing effect is best. It may be because the molar ratio of epichlorohydrin and dimethylamine has a great influence on the degree of cationization of the polymer, and the molecular weight of the polymer also changes with the amount of the monomer, thereby affecting the fixing effect. When the molar ratio of dimethylamine to epichlorohydrin is 1:1.5, the degree of cationization of the polymer is higher, the molecular weight is larger, and the color fixing effect is better. 2.1.2 Effect of reaction temperature on the performance of fixing agent According to the synthesis method of 1.3 fixing agent, the synthesis experiment was carried out, and dimethylamine and epichlorohydrin were added in a molar ratio of 1:1.5, and the reaction was carried out for 2 hours. , adding 4% of the total mass of the reaction monomer of tetraethylene pentamine, after reacting for 2 h, changing the temperature of the reaction after heating, continuing the reaction for 5 h, and solidifying the obtained series of products to directly cotton fabric dyed directly by Lake Blue 5B Color treatment, test its color fastness, the results are shown in Table 2. 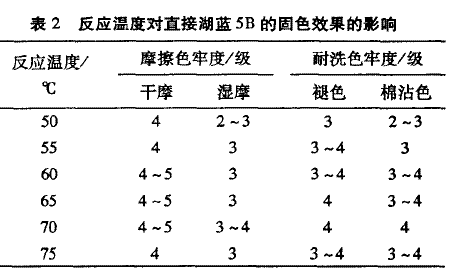
It can be seen from Table 2 that with the gradual increase of the reaction temperature, the color fastness is improved, and the reaction temperature is in the range of 70 °C. The temperature is low, the reaction is insufficient, and a product with a high degree of polymerization cannot be obtained. The temperature is high, the polymerization rate is fast, the molecular weight of the polymer increases rapidly, and the viscosity increases. When applied to dyed fabrics, it is easy to cause intermolecular aggregation. It is difficult to enter the fiber interior, and the fixing agent reacting with the dye is correspondingly reduced. The color effect is declining. Therefore, the reaction temperature must be strictly controlled during the synthesis process.
2.1.3 Effect of reaction time on the performance of fixing agent According to the synthesis method of 1.3 fixing agent, the synthesis experiment was carried out, and dimethylamine and epichlorohydrin were added in a molar ratio of 1:1.5, and the reaction was carried out for 2 hours. , adding tetraethylene pentamine which accounts for 2% of the total mass of the reaction monomer, and after heating for 2 hours, the temperature is raised by 70 ° C, and the reaction time after adding tetraethylene pentamine is changed, and the obtained series of products are respectively dyed directly to Lake Blue 5B. The cotton fabric was fixed and tested for color fastness. The results are shown in Table 3. 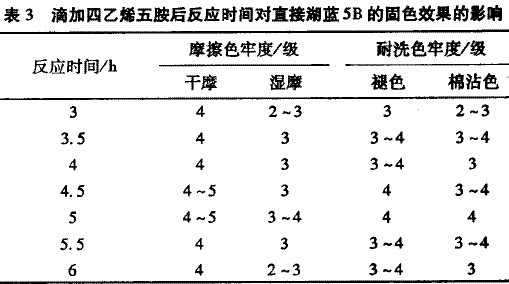
It can be seen from Table 3 that with the extension of the reaction time, the fixing effect becomes better. When tetraethylenepentamine is added dropwise, the reaction is carried out at 70 ° C for about 5 h, and the effect is optimal. After adding tetraethylenepentamine to the reaction for 5 hours, the polymerization in the system is complete, and the reaction continues, which not only causes waste of energy, but also causes excessive side reactions in the reaction system due to long-term reaction at high temperature, so that the final product does not Pure, and the viscosity of the polymer is too large, the fixing effect is reduced when used.
2.2 Fixing process The dyed cotton fabric of the direct dye lake blue 5B (dye concentration 10% O.w.f.) was fixed by the synthesized polyamine type fixing agent, and the friction of the cotton fabric after the finishing was tested. Color fastness and wash fastness, optimized for fixing process to determine the best fixing process for direct dyes.
2.2.1 Amount of fixing agent The polyamine-type fixing agent is used to treat the direct lake blue 5B dyed cotton fabric at different dosages. The measured color fastness of the fabric is shown in Table 4. 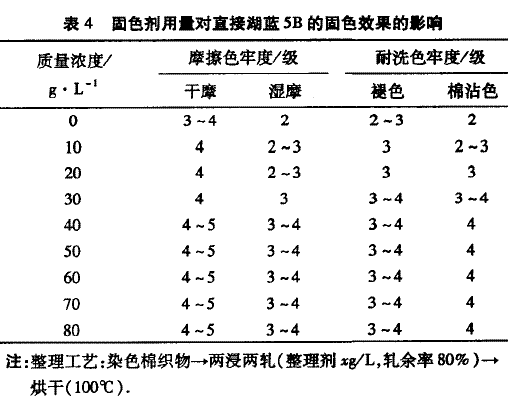
It can be seen from Table 4 that at the mass concentration of 0g/L to 40g/L, the color fastness of the dyed fabric increases with the concentration of the fixing agent, which may be due to the amount of fixing agent reaching 40 L. When it is left and right, the fixing agent can be fully combined with the fiber and the dye, and the amount of the fixing can not reach the proper fixing effect. Continue to increase the amount of fixing agent, the color fastness does not change much after reaching 4og/L. Therefore, considering the comprehensive cost, it is best to choose 40g/L for the fixing agent.
2.2.2 Drying temperature Polyamine-based fixing agent is used to treat the direct lake blue 5B dyed cotton fabric at different drying temperatures. The measured color fastness of the fabric is shown in Table 5. 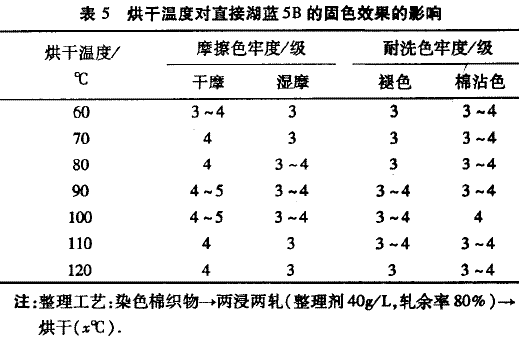
It can be seen from Table 5 that the fixing effect is best when the drying temperature is 100 °C. The reason for the analysis may be that the fiber and the fixing agent are just able to maintain their optimum performance at a temperature of 100 °C. When the temperature is lower than the temperature, the fiber and the fixing agent cannot be fully combined, so that the fastness is not good. Above 100 ° C, the temperature is too high, the structure of the fixing agent is destroyed, and the fiber may be damaged to some extent, resulting in a decrease in the fixing effect.
2.2.3 Rolling rate The polyamine-type fixing agent was used to treat the direct lake blue 5B dyed cotton fabric under different rolling ratios. The color fastness of the fabric was measured as shown in Table 6. It can be seen from Table 6 that the fixing effect of the fixing agent is best when the rolling ratio is about 80%. The reason may be that within a certain range, as the liquid loading rate of the fabric increases, the more the fixing amount remains on the fabric after rolling, the more the bonding between the fixing agent and the dye is. After the rolling ratio exceeds 80%, the liquid-carrying rate is too high, and a large amount of fixing color remains on the fabric, which makes the fixing effect worse. 
In summary, the optimal fixing process of the self-made polyamine fixing agent applied to the direct dyed cotton fabric is as follows: dyeing cotton fabric one or two dip two rolling (finishing agent 40g/L, rolling rate 80%)→ Drying (100 ° C).
2.3 Comparison of fixing effect In order to understand the fixing performance of the self-made polyamine fixing agent and truly reflect the practical value of the fixing agent, this experiment compares the self-made fixing agent with the aldehyde-free fixing agent 2011. The test results were shown in Table 7 by testing the dry and wet rubbing fastness and the fastness to washing of the directly dyed cotton fabrics of Lake Blue 5B (dye concentration 10% O.w.f.). 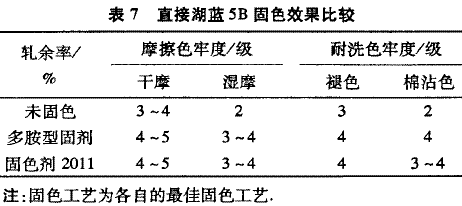
It can be seen from Table 7 that the polyamine-based fixing agent synthesized in this experiment has improved wash fastness compared with the mature aldehyde-free fixing agent 2011, and other fixing properties are similar, which can make direct dyes. The color fastness is improved by 1-2.
2.4 Changes in the color of the fabric after finishing the fixing agent The color change of the cotton fabric after finishing by the fixing agent is shown in Table 8. 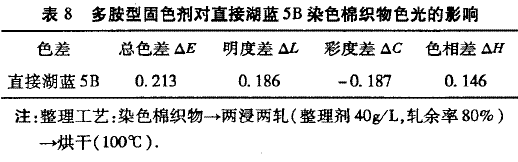
It can be seen from Table 8 that after finishing by the fixing agent, the color of the fabric changes slightly, but the change is not big. It may be because the dyed fabric is immersed in the process of the polyamine type fixing agent finishing liquid, and some dyes fall off and the amount of dye on the fabric changes. After the dyed fabric is impregnated with the fixing liquid, the dye coloring system is subjected to high temperature and chemical action during drying, and may be destroyed, thereby causing color change. 3 Conclusions (1) The optimal synthesis process is as follows: after reacting dimethylamine and epichlorohydrin with a molar ratio of 1:1.5 at 28~C for 2 hours, adding 4% of the total monomer mass of tetraethylene Pentaamine, continue to react for 2h, then warmed to 70 ° C reaction for 5h, that is, a polyamine type fixing agent is obtained. (2) The best fixing process is: dyed cotton fabric → two dip two rolling (finishing agent 40g / L, rolling rate 80%) → drying (100 ° C). The fastness of the direct dye-dyed cotton fabric after fixing by color is improved by 1 to 2 grades, and the color shade changes are small, which has a good application prospect.
references:
[1] Deng Yaoming. Synthesis and properties of aldehyde-free fixing agent [J]. Journal of Dongguan University of Technology, 2009, 16:88-92.
[2] Huang Maofu, Yang Yuqin. Development and current situation of aldehyde-free fixing agent [J]. Printing and dyeing auxiliaries, 2002 (4): 1-4.
[3] Yang Hua. Development and application of aldehyde-free fixing agent [J]. Fine chemical raw materials and intermediates, 2007 (6): 15 a l8.
[4] Liu Weiwei, Zhang Wei. Low aldehyde and no aldehyde printing and dyeing auxiliaries [J]. Hebei Textile, 2009 (2): 69-73.
[5] Huang Xinzhao, Zhang Zhongyi, Zhang Xiaodong. Application of dimethylamine polymer in fixing and flocculation [J]. Journal of Qingdao University, 2008(1): 56-. 62.
[6] Li Zhanxiong, Wang Changyu, et al. Preparation and application of a cationic aldehyde-free fixing agent [J]. Printing and dyeing auxiliaries, 2007 (24): 10-12.
[7] Yang Jingxin, Chen Xinhua. Development and application of polycationic aldehyde fixing agent [J]. Printing and dyeing auxiliaries, 2009, 26: 23-26.
Coal Activated Carbon For Water Purification
Use: Usedin the purification of drinking water, in-depth treatment of water water etc.
Spec.:
|
Model NO.
|
Moisture(%)
|
Strength(%)
|
Idine value(mg/g)
|
methylene blue value(mg/g)
|
Ash(%)
|
Packing density(g/L)
|
pH-value
|
Grain diameter(mm)
|
| DX-3060 |
≤3
|
≥90
|
≥950
|
≥140
|
≤10
|
530±20
|
8-10
|
Φ1.5
|
| DX-3070 |
≤3
|
≥90
|
≥950
|
≥150
|
≤10
|
500±20
|
8-10
|
-
|
| DX-3080 |
≤3
|
≥90
|
≥950
|
≥150
|
≤10
|
490±20
|
8-10
|
-
|
| DX-4060 |
≤5
|
-
|
≥950
|
≥150
|
≤15
|
-
|
8-10
|
-
|
| DX-4070 |
≤5
|
-
|
≥950
|
≥150
|
≤15
|
-
|
8-10
|
-
|
Coal Activated Carbon For Water Purification
Coal Activated Carbon For Water Purification,Coal Columnar Activated Carbon For Water Purification,Activated Carbon For Water Purification,Activated Carbon For Industrial Water Purification
SHIZUISHAN ZhongShi activated carbon co,.ltd , http://www.zscarbonchina.com