The aero engine is the heart of the aircraft and is one of the determining factors in aircraft performance. Because the fighter engine needs to work repeatedly for a long time in the environment of high temperature, high pressure, high speed and high load, and also requires the characteristics of light weight, small volume, large thrust, safe and reliable use, and good economy, it is currently in the world. The only countries that have independent engines for independent development are the United States, Russia, Britain, France, and the middle. The development of China's aero-engines was developed on the basis of a blank after the founding of the People's Republic of China. From the initial imitation, improvement, and modification to today's design and manufacture of high-performance aero engines, we have gone through a development path full of thorns. .
According to the "three scoops" of the gourd painting

The turbojet 5 engine is the first turbojet engine imitation of China based on the technical data of the former Soviet BK-1φ engine, which was developed by Shenyang Aero Engine Factory. The turbojet 5 is a centrifugal, single-rotor, afterburning aero engine with a maximum thrust of 25.5 kN, an afterburning thrust of 32.5 kN and a weight of 980 kg. It is mainly used for domestic æ¼-5 fighters. . The turbojet 5 engine uses a large number of high-strength materials and high-temperature resistant alloys, and the nozzle processing technology requires high precision, complex blade profiles, and intensive combustion chamber thin-wall welding and other advanced manufacturing techniques. Ability is a test. After all aspects of cooperation and efforts, the first batch of turbojet 5 engines passed the appraisal in June 1956 and began to put into mass production, which was more than a year earlier than the original plan. It has played a very good role in the smooth production of the domestic æ¼-5 fighter. The key role. The successful development of the turbojet 5 engine marks that the Chinese aero-engine industry has evolved from the era of manufacturing piston engines to the era of jet engines, becoming one of the few countries in the world that can mass-produce jet engines. .

The turbojet 6 engine is an afterburning turbojet engine manufactured by China according to the technical data of the PII-9B engine provided by the former Soviet Union. It is mainly used for the domestic J-6 fighter and the strong-5 attack aircraft developed later. Compared with the turbojet 5 engine, the turbojet 6 has greatly improved in performance, from subsonic speed to supersonic speed, and the structure of the compressor has also evolved from centrifugal to axial flow, with a maximum thrust of 25.5 kN. The afterburning thrust is 31.8 kN, although it is not much different from the vortex jet 5, but the weight is reduced by 23%, only 708 kg, the diameter is also shortened by 48%, greatly reducing the windward area of ​​the aircraft, suitable for æ¼-6 Supersonic flight. Although the first engine of the turbojet 6 was assembled in 1958, due to the influence of the "Great Leap Forward" movement at the time, a series of quality problems occurred in the turbojet 6 engine, 60 engines delivered in March 1959. The continuous exposure of serious quality problems caused the entire æ¼-6 aircraft of the entire army to be grounded. In 1960, the Central Military Commission decided to carry out a total quality rectification of the Shenyang Aero Engine Factory and re-test the turbojet 6 engine. In October 1961, the re-commissioned turbojet 6 engine passed the full-life test, and then transferred to mass production. 72 units were delivered in the same year, which guaranteed the requirements of the J-6 aircraft. However, because the turbojet 6 engine is based on the engine data provided by the former Soviet Union, it also has some defects in the former Soviet engine. It was not until 1970 that Shenyang Aero Engine Factory completely solved all kinds of problems in use, and once again improved the maneuverability of the J-6 aircraft. Then, three models of turbojet 6 and turbojet 6A/B were developed.

The turbojet 7 engine was manufactured according to the technical data of the P-II-300 engine supplied by the former Soviet Union, and was mainly used for the 2x sonic -7 aircraft developed at that time. The performance of the turbojet 7 engine is greatly improved compared with the turbojet 6. The maximum thrust is 38.2 kN, and the afterburning thrust is 55.9 kN, which is 50% and 77% higher than that of the turbojet 6, respectively, and is axial flow. Double-rotor structure with 6-stage low-pressure air machine and 2-stage turbine to form two rotors of high pressure and low pressure. The flame tube adopts the film cooling type, and the afterburner is also improved, which eliminates the shortcoming of the high-altitude afterburning instability of the turbojet 6 engine. The adjustment of the tail spout is controlled by an automatic device, and more new materials are used on the material, such as stainless steel and superalloy, respectively, for the compressor and the turbine blades. Whether in performance or in structure, the turbojet 7 is more complex than the turbojet 6, and the requirements for the manufacturing process are more stringent. In 1965, the development of the turbojet 7 was fully carried out. Due to the sufficient preparatory work in the early stage, the trial production work progressed smoothly. In October of the same year, the first engine was assembled. In December 1966, through technical appraisal, mass production began.
In 1970, it was changed to Guizhou Aero Engine Factory. In the later period, Guizhou Aero Engine Factory carried out several innovations on the technology of turbojet 7 engine, which greatly improved the performance and quality level of turbojet 7. Then with the demand for the power plant of the J-8 aircraft, China has successfully developed the turbojet 7 A-type engine, which successfully realized the transition from simple imitation production to self-design and modification.
Half a trip to the "one grass"

In 1964, China began the development of a new generation of fighters and attack aircraft, namely the development plan of the -9 and -6. To this end, Shenyang Aero Engine Design Institute proposed a total of 22 design schemes for two-axis turbojet, uniaxial turbojet and turbofan. After screening, it is concluded that only turbofans can meet the performance requirements of these two aircraft. , é‚ named it a turbofan type 6 engine. This is the first time that China has designed a large thrust engine. It is designed as a two-shaft internal and external culvert hybrid afterburning turbofan engine. The designed maximum thrust is 70.6 kN, the afterburning thrust is 121.5 kN, and the thrust-to-weight ratio is 6. 6 Initial design began in October 1964, and all drawings were completed in 1966. At the beginning of 1966, prototypes were prototyped by Shenyang Aero Engine Factory. In 1969, the manufacture of two test machines was completed. The initial commissioning of the turbofan 6 began in 1968. The entire commissioning work includes five parts: operation test, performance commissioning, long-term test, high-altitude and flight test, and national final test. During the five years of operation and commissioning, problems such as poor performance of the compressor components and small surge margin of the high-pressure compressor, and start-up and medium-speed surge were solved. In 1974, the engine reached 100% speed and entered the high speed running test. However, at this time, there were problems such as high-pressure rotor vibration, high-speed surge, and temperature before the turbine exceeded the design value. In November 1979, various problems occurred were solved one after another, and the engine achieved high-speed and long-term stable operation. In 1980, the turbofan 6 began to enter the performance test stage. In 1981, the afterburner test was carried out, and the engine afterburning thrust reached 123.5 kN, achieving the design performance of the afterburning state. In 1973, due to the modification of the design specifications of the J-9 aircraft, the performance has been further improved (up to double 2.5, that is, the limit of 25,000 meters, the speed of Mach 2.5), plus to meet the æ¼-13 aircraft launched in 1976 In the development of the need, in 1980, a modification of the turbofan 6 engine, namely the turbofan 6G, was drafted. The improvement work is mainly to increase the maximum thrust of the engine to 138.2 kN while maintaining the original engine dimensions, the maximum thrust is increased to 83.3 kN, and the thrust-to-weight ratio is increased to 7.1982 in February, the first turbofan 6G The ground test, the measured maximum thrust and afterburning thrust have reached the expected indicators, can carry out actual flight test, paving the way for further development. However, in the early 80s, due to changes in the air force equipment system, the -9 and -6 aircraft plans were successively dismantled, and the turbofan 6 as its supporting power also lost its use. In July 1983, the development of the turbofan 6 engine was completely suspended. At the beginning of 1984, the development plan was officially cancelled.
Self-developed "three treasures"

The development of the turbojet 13 series engine has made China end the history of not being able to develop and produce high-performance turbojet engines. Although its performance and technology are not particularly advanced, it is an important transition from imitation to self-design. After entering the 1980s, China's aero-engine development capability has already possessed certain strength, and this period is also a crucial moment for the development of China's new æ¼-8II and æ¼-7III aircraft. Due to the increased performance requirements of the aircraft, a new engine must be used as the power unit for both aircraft, so the turbojet 13 is "born". The turbojet 13 engine has greatly improved the structure of the compressor, which has greatly improved the surge margin. The low-pressure rotor has an inter-shaft bearing, and the vibration is small. The compressor rotor disk and the blade use a large amount of titanium alloy, which reduces the vibration. The weight increases the working strength of the blade. In addition, more advanced engine control devices have been added to improve engine control performance, reliability and stability. The thrust of the engine has also increased to 43.1 kN, and the afterburning thrust has reached 64.7 kN, which is 50% and 15% higher than that of the turbojet 7, and the engine repair interval has reached 350 hours. The development of the turbojet 13 engine began in 1978. In 1980, the first batch of three engines began to test the vehicle. In 1984, the reliability test was completed. In 1985, the test flight was completed, which satisfied the æ¼-8II aircraft. Development progress. In the late 1980s, the improved turbojet 13A engine was also developed. The main direction of improvement was to improve performance and reliability, and many measures were taken. The improved engine front turbine temperature was increased by 50 degrees and the engine's afterburning thrust was increased to 64.7 kN. A number of tests have shown that the turbojet 13A engine has good matching, stable operation and significant improvement in reliability. In 1991, Turbojet 13A began to enter mass production, becoming the standard power of the æ¼-8B, a modified æ¼-8II. Later, the turbojet 13F engine, the turbojet 13FI engine, and the turbojet 13AII and turbojet 13B models were developed. It is worth mentioning that the turbojet 13B engine, the performance of all aspects of the engine is the best performance of the turbojet 13 series, mainly in the compressor, casing, turbine blades and afterburner has made significant improvements. The engine's afterburning thrust increased to 68.6 kN, and the fuel consumption rate dropped by 2.5%, reaching the original design goal.
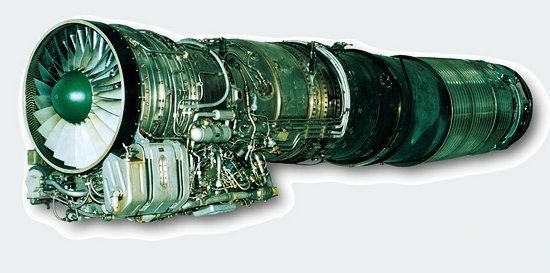
The “Kunlun†engine is the first domestically produced turbojet engine designed and developed by itself. It has complete “independent intellectual property rights†and its technology, materials and processes are based entirely on the domestic market. The development of the "Kunlun" engine has some accidental factors, and it is very difficult to have this result today. In 1984, the superior issued the task of developing the "Kunlun" engine verification machine. Formally established in 1987, began to enter the development stage of the prototype. At this time, China has promulgated a "new engine general specification". The higher level requires that the development of the "Kunlun" engine should fully implement the new national military standard, which makes the development progress of the "Kunlun" engine greatly slowed down. During the "Kunlun" engine's ground interview vehicle, there have been problems such as high-pressure turbine blade breakage, high-pressure compressor and low-pressure compressor blade breakage, engine pipeline leakage oil, excessive air lubricant consumption, and high bulkhead temperature. In the installed test flight, various major technical problems such as partial afterburning pulse, low-increment ignition success rate, high-altitude large-speed surge parking, high-altitude small-speed cut-off and after-loading have appeared. After nearly a year of research and development, the company's technical personnel have successfully solved all the technical problems that have emerged. The development work has also entered the final stage. Finally, it passed the national test in December 2001 and officially designed and finalized in 2002. 18 years. Later, China has successively launched the "Kunlun" I and "Kunlun" II engines. In particular, the "Kunlun" II engine has a maximum thrust and afterburning thrust of 53.9 kN and 76.4 kN, respectively, compared with the "Kunlun" engine, and the fuel consumption rate of the maximum thrust and afterburning force is reduced to 0.093. The kilograms/bull "hours and 0.18 kilograms/bull" hour, the thrust-to-weight ratio is 7. Since the installation and size of the "Kunlun" II engine are basically the same as those of the large number of turbojets and turbojet 13 engines in service in China, It is very interchangeable, so it can be easily installed on all types of æ¼-7 and æ¼-8 aircraft in active service, which makes the performance of these two aircrafts have a leap-forward improvement, greatly improving our sea and air force. Airborne air combat capability.

After the introduction of “Sbei†MK202, Xi’an Aero Engine Factory was responsible for the trial production. It is called the turbofan 9 engine in China. With the smooth development of the J-7 aircraft, dozens of "Speer" MK202s were introduced to the first batch of aircraft. Subsequently, in order to meet the needs of the future production modification of the J-7, Xi'an Aero Engine (Group) Co., Ltd. began to carry out the comprehensive localization of the turbofan 9 in the early 1990s. In November 1995, part of the domestically produced turbofan 9 engine successfully completed the 150-hour test, but at this time the localization rate of the turbofan 9 reached only 70%, and some equipment could not be produced. Therefore, in the second half of 1999, the full localization of the turbofan 9 engine was started. The West Air Group Company has successively overcome a series of technical difficulties such as precision casting (forging) non-remaining hollow volume blades and digital electronic control system. The ignition started; the 150-hour process test started immediately in early 2001. The test results showed that the performance and technical indicators met the test acceptance criteria. The domestically-made turbofan 9 engine was renamed the “Qinling†engine. On the morning of June 1, 2002, the "Qinling" engine, which was condensed with the innumerable blood and sweat of Xihang Airlines, made its first flight successfully, and then passed dozens of subjects, indicating that the engine's performance and stability met the predetermined requirements. . In July 2003, the “Qinling†engine localization project passed the technical appraisal in Xi'an, which ended the blank of China's domestic turbofan engine equipment.
"A knife"

In the early 1980s, the China Aviation Research Institute was dismantled due to the æ¼9, æ¼13 and other projects that were launched in the 1970s. The turbofan 6 series engine that was developed for 20 years was also forced to dismount due to the absence of assembly objects. As a result, China’s gap in fighter power and developed countries has been more than 20 years. In the face of the severe situation in the Chinese aviation industry, the country decided to develop turbofan 10 series engines in the mid-1980s. According to different assembly objects, the turbofan 10 series has turbofan 10, turbofan 10A, turbofan 10B, turbofan 10C, turbofan 10D and other models. The turbofan 10A is specially designed for China to catch up with the world's advanced level.æ¼ matching. In order to speed up the development of the turbofan 10 series engine, China adopted the two-legged approach: First, the introduction of mature foreign core machine technology. In the 1980s when Sino-US relations improved, China imported aero-enginedurable land-fired steam turbines of the same class as F100 from the United States. This is one of the important technical sources of the turbofan 10A core machine; China made full use of the high-precision research results that were being carried out at that time (such as the successful push-through core machine technology in 1992, the performance requirements exceeded F404 in all aspects), and improved the introduced core machine to make the core machine technology and the US prototype happen. A big change, the performance is greatly enhanced. The turbofan 10/10A is a three-stage fan, 9-stage rectification, 1 high-voltage, 1 low-voltage, 12-stage, single-stage high-efficiency high-power high-low pressure turbine, the so-called 3+9+1+1 structure. The high thrust-to-weight ratio is lower than the advanced engine. The engine was successfully developed with transonic fan; air-cooled high-temperature blade, electron beam welding integral fan rotor, titanium alloy precision casting machine; extruded oil film bearing, brush seal, high-energy ignition nozzle and whole unit Advanced technologies such as body design. Among them, the turbine blade adopts the advanced material of directional solidification high-temperature alloy, and the advanced technology of porous reflow composite cooling which adopts the convection and front edge impacting gas-filling membrane "three-in-one", the cooling effect of the turbine blade is doubled. Although the turbine blade of the turbofan 10 is a directional crystallized DZ125, it adopts China's original low segregation technology, and its comprehensive performance is comparable to that of the first generation of single crystal superalloy. However, there are also deficiencies. The biggest disadvantage is that the turbine blades have hollow portions, and some portions are thin, and cracks are easily generated between the columnar interfaces during solidification, which limits manufacturing. However, in general, the performance parameters of the turbofan 10A are second to none in China, which also makes China's aviation power industry reach the level of the developed countries in the mid-1980s, and has a milestone significance in the history of China's aviation engine development.
SUNPLUS Gold Paper is made with premium aluminum oxide grains, high quality latex paper and strong resin. Its special stearate coating is designed to prevent clogging and reduce dust problem. It is very well suited for high speed sanding in a wide range of applications.
Founded in 2004, Sunplus has developed into an enterprise with the leading fully - automated Germany system production line and technology to make high and stable quality sandpaper. All our materials are imported from Europe, Japan and Korea, which assures high quality products from the source.
We constantly invest in research and development so as to ensure that our products will always be a step ahead of competition.
Gold Paper,Gold Sand Paper,Gold Sandpaper,Gold Paper Sandpaper
GUANGZHOU SUNPLUS TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.sunplussandpaper.com