1. Litchi and longan balanced fertilization and blending ratio
Lychee and longan are perennial evergreen fruit trees with long growth and development cycles and large growth results. It has the characteristics of storage nutrients and nutrient reuse, and requires a large amount of nutrient supply to ensure vigorous growth and meet the high-yield, high-quality and high-quality nutritional needs. Therefore, it must be supplemented by continuous fertilization. However, the supply of fertilizer nutrients must be comprehensive and appropriate, all kinds of nutrients should be fully matched, the proportion should be moderate, all kinds of nutrients are equally important, and all of them will affect the growth and yield of trees. Many studies have confirmed that the yield of litchi and longan does not increase with the increase of fertilizer application. The two are not linearly related, but have a curvilinear relationship. When the amount of fertilizer reaches a certain level, the yield does not increase and continues to increase. When the amount of fertilizer is applied, the yield decreases. Moreover, various nutrients need to be matched with each other in a certain proportion when the tree grows and the flowering result of the yield is formed. According to relevant data analysis, the ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients in litchi fruits is 1 :0.3~0.5:1~1.5; the ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients in longan fruits is 1:0.35~0.5:1.5~2.15 . According to the theoretical push algorithm, estimation method and field test method, the fertilization amount and the ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in litchi and longan are 1:0.3~1:1~1.5; the longan is 1:0.5~1:1.5~2.0. According to the fertilization level of domestic litchi and longan, the ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in litchi is 1:0.5~0.6:1~1.5; the ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in longan is 1 :0.4~0.6:1.3~1.5. Although the above three cases are different, the ratios of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium are relatively close.
The adult lychee tree produces 100 kilograms of fruit, and the annual nitrogen application rate is 1~1.5 kg . The ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium (N :P2O5:K2O) is 1:0.5~1:1.2~2.0; adult longan result tree The plant produces 100 kilograms of fruit, and the annual nitrogen application rate is 1~1.8 kg . The ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium (N :P2O5:K2O) is preferably 1:0.5~1:1.5~2.2. The above is for reference application, and each production area can be corrected according to actual production conditions.
Second, litchi, longan fertilization period
During the fertilization period of litchi and longan, it is necessary to make timely and appropriate fertilization according to the fertility characteristics, fertilizer characteristics and environmental impact of different varieties and different ages, so as to give full play to the effect of fertilization. The juvenile tree and the tree that enters the fruiting stage and the adult fruit tree that enters the abundance period have different growth and development characteristics, and the choice and demand for nutrients are different. Therefore, not only the amount of fertilizer applied is different, but also the number and duration of fertilization are different. In the annual cycle, the absorption and demand of nutrients also showed obvious seasonal changes in the phenological period. The amount and intensity of nutrient absorption were lower in the early stage of spring bud germination, but with the growth and flowering of roots and shoots. As a result, the absorption and demand for nutrients gradually increase and reach the highest peak, and the absorption of fruits after maturity and autumn and winter will gradually decrease. Moreover, in the new shoots, the nitrogen uptake was more; during the flower bud differentiation and flowering, the young fruit absorbed more phosphorus; during the fruit expansion period, the potassium absorbed more. Therefore, the fertilization in each period should be different according to its characteristics, the amount of fertilizer applied, the type of fertilizer and the mix of fertilizers.
1. Young tree fertilization period The sapling fertilization period is different from the result tree. Fertilization of young trees is to meet the needs of vegetative growth and rapid expansion of the canopy and the cultivation of canopy area. Not only the amount of fertilizer should be increased year by year, but also the proportion of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium should be adjusted, and the number and timing of fertilization should be adjusted. The fertilization period is mainly around several times of shoots and roots. Generally, a small amount of thin and thin fertilizer is applied. Especially in the first year after planting, it is best to apply 1 month after planting until September to October. The second thin human excrement or thin urea solution, combined with the expansion of the hole in the winter to apply soil 1 organic fertilizer, 7-8 times a year. The high temperature and rain in South China, the saplings grow fast, the number and number of shoots are many, and the fertilizer is decomposed quickly, the amount of permeation is large, and the number of fertilization can be increased appropriately. As the age of the tree increases, the amount of fertilizer should be gradually increased, and the proportion of phosphorus and potassium should be appropriately increased. In the past few years, nitrogen fertilizer was the main factor, and in the next few years, the amount of phosphorus and potassium was increased. The number of fertilization is mainly around several times. The spring shoot is the basis of the subsequent shoot growth. Before the spring shoots, the organic fertilizer should be applied as the base fertilizer, and the amount of fertilizer should be increased appropriately. The summer and autumn shoots should be mastered before and after the shoot. The amount, especially the autumn shoots, as the age of the tree increases, enters the trial period of the result (small results at the beginning), and the fruit tree begins to be put into production. The autumn shoot is the result of the leap year, and the nitrogen fertilizer should be appropriately added before the autumn shoot. After the shoots are fully enriched, the phosphorus and potassium fertilizers are appropriately increased to reduce the nitrogen fertilizer. The autumn shoots of the longan are generally extended from the summer shoots. Therefore, fertilization at the summer shoots is also very important. Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers should be added after the summer shoots are taken. In June, combined with expansion of the hole to change soil, applied organic fertilizer and green fertilizer to suppress green.
The put into operation tree, which is put into the result, is in the stage of vegetative growth and reproductive growth. The fertilization should be combined with root promotion, shoot promotion, control of summer shoots and stable fruit to coordinate the balance of vegetative growth and reproductive growth of the tree. During the fertilization period, the fertilizer should be applied before the flower, the fruit fertilizer should be stabilized, the fruit should be promoted, the fertilizer should be harvested before or after the fruit harvesting, Mainly around the spring shoots and autumn shoots, and control the summer shoots to prevent fruit drop. In addition, juvenile trees and put into production trees can be combined with multiple foliar fertilization from March to August to promote tree roots through roots.
2. Adult fruit tree fertilization period   Adult trees have entered the production period of comprehensive results, and fertilization should be based on the recovery of yield and tree potential to prolong the maturity of the results. According to the age of the tree, the tree potential, the target yield, according to the demand for nutrients in each phenological period, focus on cultivating the good results of the mother branch, promote the differentiation of flower buds, and timely fertilize with the goal of keeping flowers and strong fruits.
(1) Litchi adult tree fertilization period According to the ecological conditions of litchi production in China and the biological characteristics of litchi, the whole year of fertilization is divided into three main periods:
Pre-flowering fertilizer: The effect of pre-flowering fertilization is to promote germination and differentiation, flower ear development, increase flower mass, improve flower quality, increase earing, increase grain, reduce flowering and fruit drop, and increase fruit setting rate. This fertilization is one of the most critical periods of the year. It should be applied at an appropriate time, and the flowering of the flowering leaves should be taken early or too early; if it is too late, it will not be able to play its role. This stage of fertilization requires nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. According to the analysis of the 19-year-old "Huaizhi" litchi flower in Guangxi in 1986, after the flowering, the whole tree consumes 0.437 kg of nitrogen, 0.057 kg of phosphorus and 0.286 kg of potassium; the nitrogen consumption of falling flowers is 0.42 kg, and the phosphorus is 0.055 kg. 0.276 kg. According to the data, the lychee flower is 2.086%~2.758%, the phosphorus is 0.29%~0.492%, and the potassium is 1.275%~2.31%. According to reports, 18 to 22 years old "Lanzhu", "Wuye" and "Chen Zi" litchi were used as materials to carry out heavy fertilizer before flowering (accounting for 40%~50% of the annual application, of which nitrogen and potassium accounted for each 50% of the annual application, phosphorus accounted for 40% of the annual application) and general fertilization (1/3 of the pre-flowering application). The results showed that the “Chen Zi†lychee and “Wuye†lychee had the highest yield and the best effect before flowering. The "Chen Zi" lychee flower before the application of heavy fertilizer increased yield by 65.7% compared with general fertilization (control), "Uye" lychee increased yield by 51.8%, "Lanzhu" lychee increased yield by 31.4%, and increased fruit length and ear of fruit. In this period, in general, nitrogen and potassium account for 40%~45% of the annual fertilization amount, and phosphorus accounts for 25%~30% of the whole year.
Young fruit fertilizer: From flowering to young fruit growth and development, because the flower fruit consumes a lot of nutrients, and is in the physiological fruit drop period, at the same time, the fruit enters the rapid expansion period at the late stage of development, and the nutrient should be supplemented in time. This period of fertilization plays a role in ensuring fruit stability and strong fruit, so it is also called stable fruit fertilizer or strong fruit fertilizer. This stage of fertilization should be based on potassium fertilizer, followed by phosphate fertilizer, and with nitrogen fertilizer. According to Dai Liangzhao et al. (1986), the leaves of "Lanzhu" litchi have higher nitrogen content and lower phosphorus and potassium content, especially in the leaves of potassium. According to Ni Yaoyuan (1986), the nitrogen content in litchi leaves was higher during fruit development, and the phosphorus and potassium in leaves were significantly decreased. The above illustrates the consumption of large amounts of nutrients during fruit development, especially phosphorus and potassium, resulting in a significant decrease in phosphorus and potassium nutrients in the leaves. In this period, nitrogen application should account for 15% to 20% of the whole year, phosphorus accounts for 40% of the whole year, and potassium accounts for 30% to 40% of the whole year.
Before and after fruit picking: The main function is to restore the tree potential, reduce the leaves, promote the fullness of the autumn shoots, and promote the flower bud differentiation, and store more nutrients for the next year's flowering results. In this period of fertilization, the number of fruits, weak trees and old trees should be divided twice, and each time before and after fruit picking. The quick-acting fertilizer is mainly used before fruit picking, and the quick-acting fertilizer is combined with organic fertilizer after fruit picking. In this period, nitrogen application accounts for 35%~40% of the whole year, phosphorus accounts for 30%~40% of the whole year, and potassium accounts for 20%~30% of the whole year. In addition, foliar fertilization can be combined during the autumn shoots. Use 0.3% urea plus 0.2% ~ 0.3% potassium dihydrogen phosphate, or 0.3% ~ 0.4% potassium nitrate for rooting 2 to 3 times to promote the strong autumn shoots.
(2) Longan adult tree fertilization period Longan is the flower bud differentiation in the same year, flowering in the same year, its fertilizer needs are related to phenology. In the early spring of February in Fujian, when the spring buds of longan germinated, the flower primordium began to form flower bud differentiation, followed by flowering and fruit growth. In the longan fertilization period, there are three fertilization periods in the same year as litchi, except that the biological characteristics of the longan are shorter than the litchi, so the fertilization time is delayed accordingly.
Pre-flowering fertilizer: The purpose of fertilization before longan flower is to promote flower bud differentiation, flower ear development and spring shoot growth and increase flower mass, improve flower quality, reduce flowering and increase fruit setting. This period of fertilization is also one of the most critical fertilization periods in the year. According to Liu Xinghui et al. (1993), pre-flowering fertilizer was applied in March, mainly based on nitrogen fertilizer, combined with phosphate fertilizer and potassium fertilizer to improve flower quality and increase fruit setting rate. According to Ke Guanwu et al. (1998), longan should adopt different fertilization periods and fertilization amount to adjust the growth potential and growth amount, and apply heavy fertilizer before flowering. The inflorescence (flower stand) of longan flower spikes has been formed in the middle and late April. It is applied when it is bud. The amount of fertilizer applied accounted for 80% of the annual fertilizer use, and half of the organic fertilizer and fertilizer. Early application of heavy fertilizers provides a material basis for promoting strong fruit. According to Dai Liangzhao et al. (1989), the 17-year-old and 25-year-old "Fuyan" longan were used as test materials for different heavy-duty trials. The heavy-duty period accounted for 70% of the annual fertilizer use, and the other 30% was applied at the flowering stage. Before the experiment, the heavy fertilizer, the young fruit heavy fertilizer, the heavy fertilizer before harvesting, the heavy fertilizer after harvesting and the heavy fertilizer in winter were used in the five heavy-duty fertilizers. The results of the test for 6 years showed that the fertilizer was applied before the flower and the fruit was harvested. The effect of applying heavy fertilizer before is the best, the yield is the highest, the annual size is the least, and the effect of applying heavy fertilizer after harvesting is the worst. The yield of heavy fertilizer before flowering increased by 51.4%~62.9%, and the annual size decreased by 40.3%~53.5% (Table 1). In large-scale production, heavy fertilizer should be paid attention to before the longan flower, but the annual application rate can be adjusted appropriately. Nitrogen is the main source, phosphorus and potassium are combined, nitrogen accounts for 40%~50% of the whole year, and phosphorus and potassium account for 30%~40% of the whole year. The application period is preferably carried out in February in the big year and in March in the small year. Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â
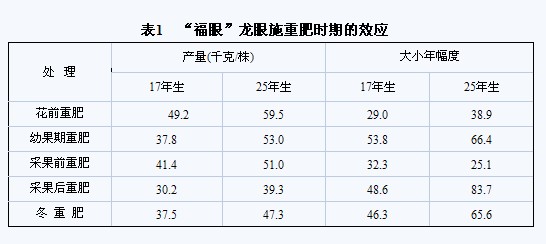
Young fruit fertilizer (or promoted fruit fertilizer): Longan consumes a lot of nutrients from flowering into young fruit. According to the analysis, the longan flower organs contained 0.74%~1.372%, phosphorus 0.169%~0.482%, and potassium 1.738%~2.652%. Flowering consumes a large amount of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients, so that the leaves and nitrogen in the flowering stage have the lowest content in the whole year. For this reason, this period of fertilization is also very important. In this period, the fertilizers are mainly phosphorus and potassium, and the nitrogen fertilizers are combined. Phosphorus and potassium fertilizers account for 40% of the annual fertilizer use, and nitrogen fertilizer accounts for 20% of the annual fertilizer use. According to Dai Liangzhao (1989), the effect of applying heavy fertilizer on young fruit is much worse than that before flowering. The 17-year-old “Fuyan†has the same effect as winter heavy fertilizer, and the 25-year-old “blessing eye†effect is also It is worse than the weight of the flower before the flower, and the size of the year is larger. From the longan needs fertilizer characteristics, this period does not have to be applied as heavy fertilizer.
Picking fruit fertilizer: picking fruit fertilizer can be divided into two types: pre-harvest and post-harvest. The purpose of applying fruit fertilizer is to promote fruit enlargement and promote the picking of autumn shoots, cultivate good results of mother branches, and restore tree potential. According to Dai Liangzhao et al. (1989), the effect of applying heavy fertilizer before harvesting fruit is also very good. Compared with heavy fertilizer after harvesting, the yield increased by 29.8%~37.1%, and the annual size was 33.5% lower than that after harvest. ~70% (Table 1). Ke Guanwu et al. (1998) pointed out that pre-harvest fertilizer should be re-applied, generally applied 10 to 15 days before fruit picking, and the application amount accounts for 20% of the annual fertilization amount, mainly based on quick-acting nitrogen fertilizer. According to research by Dai Liangzhao et al. (1989), the juvenile trees should be applied from the end of July to the beginning of August, and the Xiaonian trees should be applied in the middle and late August. The amount of fruit hanging, weak trees and old trees should be based on quick-acting fertilizer, combined with organic fertilizer, and the fertilizer is mainly nitrogen fertilizer, combined with phosphorus and potassium fertilizer. Large-scale production, the nitrogen application in this period should account for 30%~40% of the whole year, and phosphorus and potassium account for 20%~30%.
Base fertilizer: Winter base fertilizer is controversial and should be cautious. Ke Guanwu et al. (1998) pointed out that the fertilization and irrigation should be stopped from October to December after the autumn shoots were enriched to weaken the winter tree production potential and inhibit the winter draw. However, in the old longan area, the organic fertilizer is applied in the winter. The application of fertilizer in winter should be determined according to the specific conditions. Generally, the normal result tree should not be fertilized in the winter of October to December. The application of organic fertilizer can be applied before or after the fruiting, or from February to March before the flowering, but the results are more. After the fruit picking, the tree potential is slow to recover, the deciduous or weak trees, the old trees are unable to extract winter in winter, and some slow and late organic fertilizer should be applied as the base fertilizer to restore the tree potential and reduce the defoliation to promote flower bud differentiation.
Total 1 | <First <Prev 1 Next> Last> |
share to:
With the development of food culture, from simple cooking tools, gradually evolved into both use and artistic value of household articles.The classification and function of kitchen knives are more and more detailed, from the era of a Kitchen Knife fighting the world, developed into today's special combination of knives.We can provide customers all over the world with the best quality carving knives,also we can customize different carving knives according to the living habits of different countries.
Carving Knife Set,Carving Knife,Kitchen Carving Knife,Professional Carving Knife
HONG TAO KITCHEN INDUSTRY CO.,LTD , https://www.htkitchenware.com