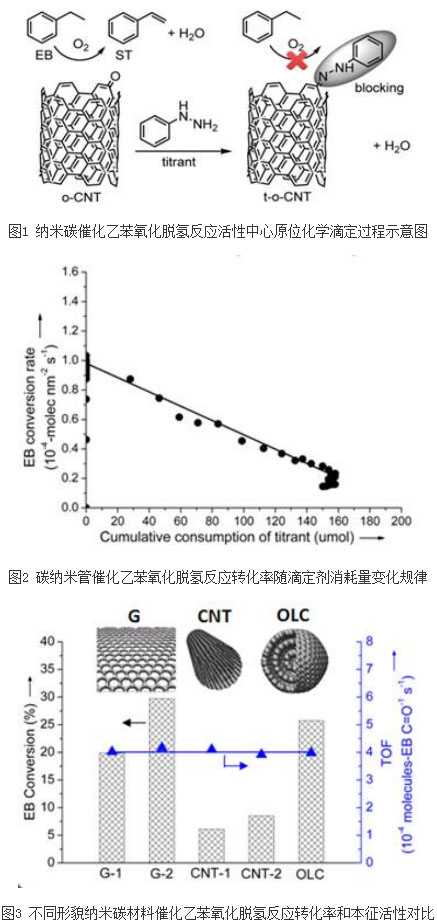
The nano-carbon material exhibits advantages such as high reactivity, high selectivity of olefin products, and long catalytic activity retention time in the oxidative dehydrogenation reaction of alkanes. As a renewable and environmentally friendly catalyst, nano-carbon materials can replace traditional metals and their Oxide catalysts are directly applied to the catalytic conversion of alkanes and other related reactions. After nearly 20 years of development, researchers have made remarkable progress in the preparation of nano-carbon catalysts and their applications in different catalytic systems, but the explanation of the catalytic nature of nanocarbons at the molecular or atomic scale, and the nanometer The evaluation and comparison of the intrinsic activity of the carbon catalyst is still unclear.
Recently, the research team led by Su Dusheng and Dr. Qi Wei, a researcher of the Catalysis Materials Research Department of Shenyang National Institute of Materials Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Metals, has made new progress in this field. Using a self-designed oxidative dehydrogenation reaction of ethylbenzene and an active center titration device, the in-situ highly selective chemical reaction between the organic small molecule and the surface active catalytic center of the nanocarbon catalyst (Fig. 1) enabled the team to successfully achieve the reaction. The quantification of the intrinsic catalytic activity and catalytically active center of the nanocarbon material under the conditions (Fig. 2). Comparing the intrinsic activity of nano-carbon catalytic materials with different morphology, it can be found that in the larger size range (bending radius of graphite layer is greater than 5 nm), the micro-morphology of nano-carbon materials (such as specific surface area and bending radius of graphite layer) The effect of intrinsic catalytic activity is small (Figure 3). The in situ chemical titration method was successfully established for the first time to determine the intrinsic activity of nanocarbon catalysts in a single experiment, which laid the foundation for detailed dynamic analysis of nanocarbon catalytic processes. The objective evaluation and comparison of the intrinsic activity of nano-carbon catalysts is the key to understanding the nano-carbon catalytic reaction process and the structure-activity relationship of nano-carbon catalysts from the molecular scale. The relevant research results were published in the form of a newsletter in the magazine Angewandte Chemie International Edition (DOI: 10.1002/anie.201505818).
Over the years, Su Dangsheng's team has been working hard to understand the nature of non-metallic nano-carbon catalysis, and they are identified in the catalytic center of nano-carbon catalytic oxidative dehydrogenation of alkanes (Science, 2008, 322, 73; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed (2013, 52, 14224), catalysts for the control of the selectivity of the reaction (Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8151) and the principles for the design and preparation of nanocarbon catalysts (Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 5782) A lot of progress has been made, and its research results have been recognized and affirmed by both domestic and foreign counterparts in the fields of non-metal catalysis and nanocatalysis.
The above research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Strategic Pilot Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Outstanding Scholar of the Institute of Metallurgy, the National (Joint) Laboratory Innovation Project of Shenyang Materials Science, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences Green Initiative.
Hexagon Thin Nut,M8 Hexagon Nuts,Hexagonal Nuts Fasteners,M39 Hexagonal Nuts
Chuangtuo Jinggong (Jiangsu) Co., LTD , https://www.chtofastener.com