Primers
During the development and construction of photovoltaic power plants, they often deal with voltages. Sometimes people hear people say 380V, and sometimes they say 400V. When do you say the former and when do you say the latter? The same applies to other voltage levels, such as 10KV and 10.5KV, 11KV, 500KV, and 550KV. This issue involves the relevant provisions of the rated voltage, the specific content is as follows:
Overview
All electrical equipment operates at a certain voltage and frequency. The rated frequency and voltage rating of electrical equipment is the frequency and voltage at which it operates normally and achieves the best economic results. According to the national standard GB/T 156-2007 "Standard voltage", the rated voltage of three-phase AC grid, generator and transformer in China is different.
First, the rated voltage of the power grid and electrical equipment
The rated voltage of the power grid is the basic basis for determining the rated voltage of various types of electrical equipment. The rated voltage level of the power grid is determined by the country according to the needs of the national economic development and the level of the power industry, after a comprehensive technical and economic analysis. Since the current is going through the line to generate a voltage drop, the voltages at the points on the line are slightly different, allowing ±5% of the voltage deviation, ie, UavN=1.05UN, and an appropriate integer, see the table below.
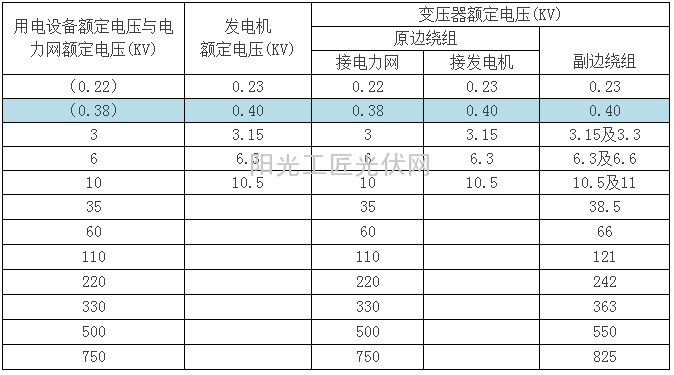
The electrical equipment is mass-produced, and its rated voltage cannot be manufactured according to the actual voltage of the circuit in use, but can only be manufactured according to the average voltage of the head and the end of the line and the rated voltage UN of the grid. Therefore, the rated voltage of the electrical equipment is the same as the rated voltage of the statistical grid.
Second, the rated voltage of the generator
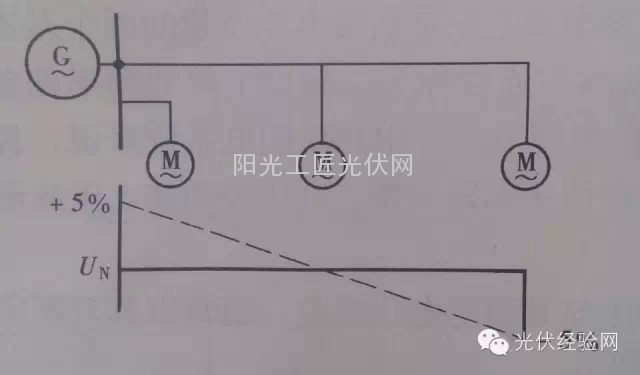
The allowable voltage deviation of the power line is generally ± 5% UN, and the entire line allows 10% of the voltage loss value, so in order to maintain the average voltage of the line at the rated value, the rated voltage of the voltage at the beginning of the line is higher by 5%, and the line The end can be 5% lower than the rated voltage of the line. Therefore, the rated voltage of the generator is higher than 5% of the rated voltage of the grid.
Third, the rated voltage of the power transformer
The rated voltage of the transformer is rather special. The voltages of the primary and secondary windings need to be defined separately.
(I) Rated voltage of primary winding
The rated voltage of the primary winding of a power transformer is divided into two situations:
1. The transformer is directly connected to the generator. At this time, the rated voltage of the primary winding of the transformer is equal to the rated voltage of the generator, ie, higher than 5% of the rated voltage of the grid at the same level.
2. The transformer is not directly connected to the generator, but is connected to the line. The primary winding of the transformer is equivalent to the electrical equipment on the line. The rated voltage of the primary winding should be the same as the rated voltage of the grid.
(II) Rated voltage of secondary winding
The rated voltage of the transformer secondary winding is also divided into two cases:
1. When the secondary winding power supply line is long, its rated voltage should be 10% higher than the rated voltage of the same-grade power grid (5% of transformer internal loss + 5% of line loss).
2. When the secondary winding power supply line is not long, the rated voltage of the secondary winding only needs to be higher than 5% of the rated voltage of the connected power grid, only considering the voltage drop of 5% inside the winding when the compensation transformer is operating at full load.
Fourth, summary
In general, the voltage follows two principles. One is the principle that the rated voltage of the equipment is equal to the rated voltage of the grid, and the other is the principle of ±5% deviation of the allowable voltage of the power line. By mastering these two principles, you can know the voltage of the relevant node and know when it is 380 volts and when it is 400 volts.
Drywall screws (sometimes called sheetrock screws) provide a stronger hold, but cost a bit more than nails. These usually feature a Phillips head. Coarse drywall screws feature coarse threads to secure gypsum boards to studs. Fine drywall screws feature smaller heads and are used to secure drywall to metal studs..
Drywall screws have deeper threads than regular screws, which prevents them from dislodging easily from the drywall. They are made of steel and require a power screwdriver to drill them into the drywall. ... W-type screws, on the other hand, are longer and thinner. They are designed for installing drywall onto wood.
Yibin Heheng Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.chinadirectfastening.com